Dependable and Autonomic Computing Platform for Managing Transactive Microgrids
Last updated on
Dec 19, 2024
This project aims to research, design and evaluate a dependable decentralized computing and communication platform to support functional and nonfunctional requirements of transactive microgrids with the focus of renewable energies. More specifically, we propose to analyze, leverage and extend DAG-based and chain-based Blockchains, smart contracts and self-adaptive paradigm to realize the proposed platform. Currently, we are building, modelling and optimizing a blockchain-based Web3 platform which aims to ficilitate the peer-to-peer energy trading which will have a great impact on renewable energy industry.
Caixiang Fan
Ph.D., Assistant Professor at The King’s University, Blockchain Researcher
My research interests include blockchain, transactive energy, and performance modelling.
Publications
BPET: A Unified Blockchain-Based Framework for Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading
In this paper, we propose and develop a novel unified blockchain-based peer-to-peer energy trading framework, called BPET. This framework incorporates microservices and blockchain as the infrastructures and adopts a highly modular smart contract design so that developers can easily extend it by plugging in localized energy market rules and rapidly developing a customized blockchain-based peer-to-peer energy trading system. Additionally, we have developed the price formation mechanisms, e.g., the system marginal price calculation algorithm and the pool price calculation algorithm, to demonstrate the extensibility of the BPET framework. To validate the proposed solution, we have conducted a comprehensive case study using real trading data from the Alberta Electric System Operator. The experimental results confirm the system’s capability of processing energy trading transactions efficiently and effectively within the Alberta electricity wholesale market.
Caixiang Fan, Hamzeh Khazaei, Petr Musilek
Fine-Grained Performance and Cost Modeling and Optimization for FaaS Applications
In this study, we therefore fill this gap by proposing formal performance and cost modeling and optimization algorithms, which enable accurate prediction and fine-grained control over the performance and cost of FaaS applications. The proposed model and algorithms provide better predictability and trade-off of performance and cost for FaaS applications, which help developers to make informed decisions on cost reduction, performance improvement, and configuration optimization. We validate the proposed model and algorithms via extensive experiments on AWS. We show that the modeling algorithms can accurately estimate critical metrics, including response time, cost, exit status, and their distributions, regardless of the complexity and scale of the application workflow. Also, the depth-first bottleneck alleviation algorithm for trade-off analysis can effectively solve two optimization problems with fine-grained constraints.
Changyuan Lin, Caixiang Fan, Nima Mahmoudi, Hamzeh Khazaei
Performance Analysis of Hyperledger Besu in Private Blockchain
In this work, we present a set of comprehensive experimental studies on Hyperledger Besu in private blockchain. We aim to exhibit its performance characteristics in terms of transaction throughput, latency, resource utilization, and scalability, from the application perspective by adding a load balancer middleware. We have carefully designed a set of comparative experiments and judiciously selected typical parameters, including transaction send rate, network size, node flavor, load balancing, consensus, and block time.
Caixiang Fan, Changyuan Lin, Hamzeh Khazaei, Petr Musilek
Performance Analysis of the IOTA DAG-based Distributed Ledger
In this paper, we have analyzed the performance of IOTA ledger using both empirical and analytical approaches. First extend an existing simulator to support realistic IOTA simulations and investigate the impact of different design parameters on IOTA’s performance. Then, we propose a layered model to help the users of IOTA determine the optimal waiting time to resend the previously submitted but not yet confirmed transaction. Our findings reveal the impact of the transaction arrival rate, tip selection algorithms (TSAs), weighted TSA randomness, and network delay on the throughput. Using the proposed layered model, we shed some light on the distribution of the confirmed transactions. The distribution is leveraged to calculate the optimal time for resending an unconfirmed transaction to the distributed ledger. The performance analysis results can be used by both system designers and users to support their decision making.
Caixiang Fan, Sara Ghaemi, Hamzeh Khazaei, Yuxiang Chen, Petr Musilek
Performance Evaluation of Blockchain Systems: A Systematic Survey
In this paper, we conduct a systematic survey on the blockchain performance evaluation by categorizing all reviewed solutions into two general categories, namely, empirical analysis and analytical modelling. In the empirical analysis, we comparatively review the current empirical blockchain evaluation methodologies, including benchmarking, monitoring, experimental analysis and simulation. In analytical modelling, we investigate the stochastic models applied to performance evaluation of mainstream blockchain consensus algorithms.
Caixiang Fan, Sara Ghaemi, Hamzeh Khazaei, Petr Musilek
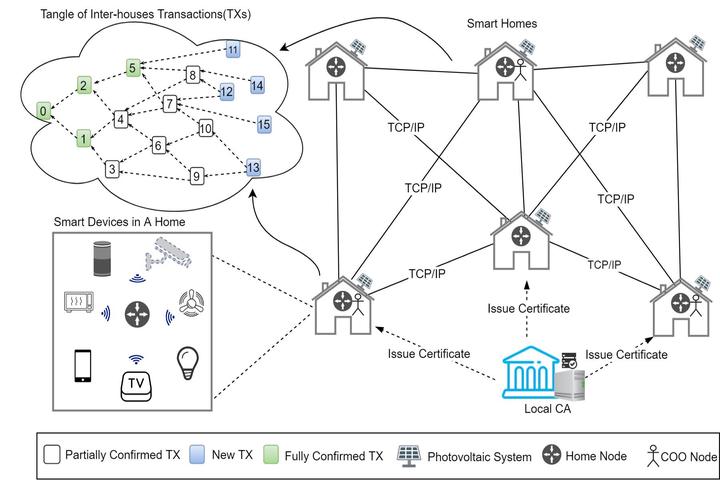
Towards A Scalable DAG-based Distributed Ledger for Smart Communities
In this paper, we propose a scalable transactive smart homes infrastructure by leveraging a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) based DLT and following the separation of concerns (SOC) design principle. Based on the proposed solution, an experiment with 40 Home Nodes is conducted to prove the concepts. From the results, we find that our solution provides a high transaction speed and scalability, as well as good performance on security and micropayment which are important in IoT settings. Then, we conduct an analysis and discuss how the new system breaks out the well-known Trilemma, which claims that it is hard for a DLT platform to simultaneously reach decentralization, scalability and security. Finally, we conclude that the proposed DAG-based distributed ledger is an effective solution for building an IoT infrastructure for smart communities.
Caixiang Fan, Hamzeh Khazaei, Yuxiang Chen, Petr Musilek
Performance Analysis and Design of an IoT-Friendly DAG-based Distributed Ledger System
In this thesis, we first conduct a comprehensive literature review on both distributed ledger technology applications in IoT and the performance evaluation of such decentralized systems. Then we present a detailed technical overview of IOTA, following a contractive review of different DAG-based distributed ledger technologies. Next, we propose a scalable transactive smart homes infrastructure by leveraging IOTA protocol and following the separation of concerns (SOC) design principle. Based on the proposed solution, an experiment with 40 home nodes is conducted to prove the concept at large scale in a cloud environment. The results show that our solution provides a high transaction speed and scalability, as well as good performance on micropayment which is important in IoT initiatives. We conduct an analysis and discuss how the new system breaks out the Blockchain Trilemma, which claims that it is almost impossible for a blockchain platform to simultaneously reach decentralization, scalability and security. Based on our findings on scalability and performance, we conclude that the proposed DAG-based distributed ledger is an effective solution for building an IoT infrastructure for smart communities, in which local residents can freely and securely transfer values.
Caixiang Fan
